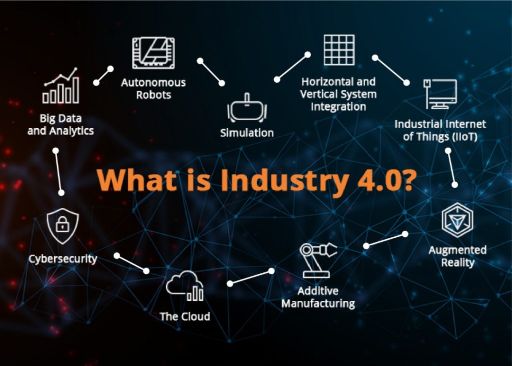
Introduction
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the advent of Industry 4.0. One of the most notable developments in this era is the concept of smart factories. These advanced manufacturing facilities leverage cutting-edge technologies and digital systems to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and drive innovation. Smart factories are reshaping traditional manufacturing operations and paving the way for a new era of industrial automation and intelligent manufacturing.
Benefits of Smart Factories
- 1. Enhanced Efficiency: Smart factories optimize production processes by automating repetitive tasks, reducing downtime, and minimizing waste. This leads to increased productivity and improved operational efficiency.
- 2. Improved Quality: With real-time monitoring and data analytics, smart factories can detect and address quality issues promptly. This ensures consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- 3. Cost Reduction: By optimizing resource utilization and minimizing errors, smart factories help reduce operational costs. Predictive maintenance also prevents costly breakdowns and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
- 4. Flexibility and Customization: Smart factories enable agile manufacturing by easily adapting to changing customer demands and product variations. This allows manufacturers to offer customized products efficiently.
- 5. Safety and Worker Well-being: Automation and robotics in smart factories can handle hazardous tasks, ensuring the safety of workers. By eliminating repetitive manual work, employees can focus on more skilled and meaningful tasks.
Challenges and Considerations

While smart factories offer tremendous advantages, there are challenges and considerations to be addressed:
- 1. Initial Investment: Implementing smart factory technologies requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure, equipment, and training. Manufacturers need to carefully evaluate the costs and long-term benefits.
- 2. Workforce Transition: The shift towards smart factories necessitates upskilling or reskilling the workforce to operate and maintain advanced technologies. Proper training programs and change management strategies are essential.
- 3. Data Security and Privacy: Smart factories generate and rely on massive amounts of data, raising concerns about data security and privacy. Robust cybersecurity measures and data protection protocols must be in place.
- 4. Interoperability and Standards: With multiple systems and technologies involved, ensuring interoperability and standardization can be complex. Collaboration among stakeholders is crucial to establish common protocols and frameworks.
- 5. Ethical Considerations: The increasing use of AI and automation raises ethical concerns, such as job displacement and the impact on the workforce. It is important to address these issues and ensure a just transition.
Conclusion
In summary, smart factories are revolutionizing manufacturing processes in the context of Industry 4.0. By combining intelligent automation, real-time data analytics, and seamless connectivity, these advanced manufacturing facilities optimize efficiency, flexibility, and quality. Embracing smart factories enables manufacturers to meet customer demands, reduce costs, and adapt to the dynamic market landscape of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.