Introduction
The manufacturing industry has gone through a series of changes over the years, with the introduction of new technologies and software. One of the latest technological advancements transforming the manufacturing environment is Smart Manufacturing. Also referred to as Industry 4.0, this innovative approach is revolutionizing how the production industry operates. Smart Manufacturing focuses on integrating different technologies to streamline processes, optimize production, and improve efficiency. The result is a manufacturing industry that is more flexible, sustainable, and cost-effective.
Smart Manufacturing has become an area of focus for many manufacturers looking to embrace the latest technological advancements and stay ahead of the competition. The goal is to establish a connected and intelligent manufacturing process, allowing manufacturers to collect and analyze data in real-time. This innovative approach is changing how manufacturers collect and analyze data, making it possible for them to identify productivity risks before they occur and take preventative measures. The beauty of Smart Manufacturing is that it elevates the manufacturer’s ability to mass produce without compromising on efficiency, customization, or quality.
Smart Manufacturing is not only transforming the production processes but also impacts the entire supply chain, starting from sourcing raw materials to distribution and customer delivery. The technology provides manufacturers with the tools to track their inventory levels and automate their ordering and delivery systems. Improved supply chain management ensures that manufacturers can produce goods to meet their customers’ demand while keeping excess inventory levels low. This level of efficiency results in reduced waste and costs associated with overstocked inventories and ordering new stocks. It also allows manufacturers to be more responsive to changes in the market.
What is industry 4.0 in manufacturing
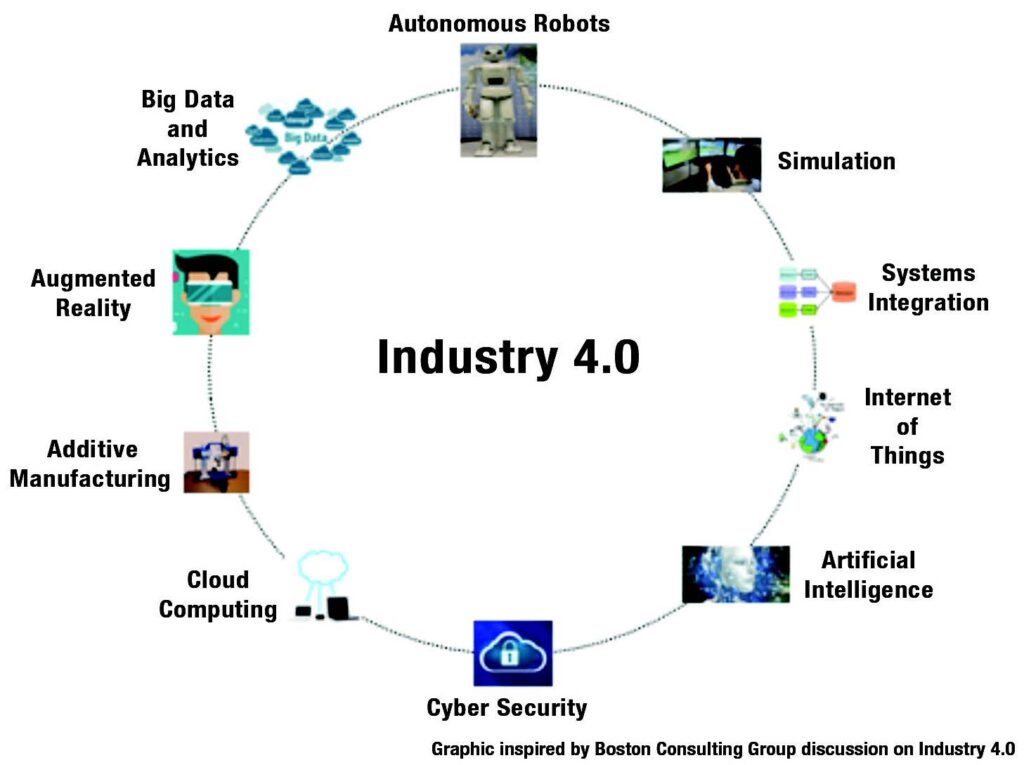
The Industry 4.0 revolution is transforming the production industry with technologies such as smart manufacturing. This approach uses intelligent automation systems, data analytics, and real-time communication to optimize production processes and enhance product quality. For instance, one of the smart manufacturing examples is predictive maintenance. Sensors and IoT devices are installed on machines to detect any abnormalities or defects in the system. This data is analyzed to predict when maintenance is needed, preventing equipment failure and reducing downtime.
Another example is the use of augmented reality (AR) in manufacturing processes. AR technology enables employees to visualize and interact with 3D models of products or equipment. With this technology, workers can see how a machine operates, identify any issues that need attention, and perform repairs instantly. This not only speeds up production but also reduces the risk of errors or accidents.
Furthermore, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the production industry by enhancing machine learning applications that can analyze vast amounts of data to improve product quality and reduce waste. AI is used to optimize energy consumption, reduce the environmental impact of production processes, and increase efficiency. With the help of advanced AI algorithms, manufacturers can make real-time decisions that drive productivity, reduce costs, and increase profitability. These technologies, along with others, are making smart manufacturing possible and revolutionizing the production industry.
Impact of industry 4.0 in manufacturing
The revolution of Industry 4.0 has transformed the manufacturing sector with advanced smart technology. Industry 4.0 has introduced the concept of a smart factory with greater communication and autonomy between machines and systems. By adopting these technologies, manufacturers can increase productivity, reduce labor costs and optimize supply chain operations.
One of the key technologies contributing to the Industry 4.0 revolution is the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT networks enable machine-to-machine communication and offer real-time data collection, allowing manufacturers to track product quality and equipment conditions. Cloud computing systems also provide remote access to real-time data and predictive maintenance analysis needed to optimize factory operations and prevent major equipment failures.
Industry 4.0 has also facilitated intelligent manufacturing through the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. AI algorithms enable manufacturers to automate decision-making processes and improve production planning, reducing time-to-market. Machine learning provides predictive modelling based on historical data, optimizing inventory management and improving production schedules. This, in turn, allows for greater customization of products and customization to meet changing market needs.
Challenges
Industry 4.0 presents both significant challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. One of the main challenges is the high cost of implementing new technologies and infrastructure required for digital transformation. This includes investing in advanced analytics, IoT sensors, and robotics, as well as upgrading existing legacy systems. Moreover, Industry 4.0 requires a skilled workforce with expertise in operating and maintaining these systems, which may be in short supply.
However, Industry 4.0 also presents several opportunities for manufacturers. It enables them to create intelligent, connected, and efficient manufacturing ecosystems that can significantly improve productivity, reduce costs, and create new business models. By leveraging real-time data analytics and machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can optimize their operations, reduce downtime, and improve quality control.
In addition, Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to create new revenue streams through the use of innovative technologies such as 3D printing, augmented reality, and blockchain. For example, 3D printing can enable manufacturers to produce parts on-demand, reducing the need for expensive inventory and supply chain management. Augmented reality can help streamline the manufacturing process by providing real-time data and remote support to workers on the factory floor. Finally, blockchain technology can help manufacturers improve supply chain transparency and traceability, which can be critical in industries such as aerospace and defense.
Overall, while there are significant challenges associated with implementing Industry 4.0, the potential benefits are substantial and can enable manufacturers to transform their businesses and gain a competitive advantage in the global marketplace.