Introduction
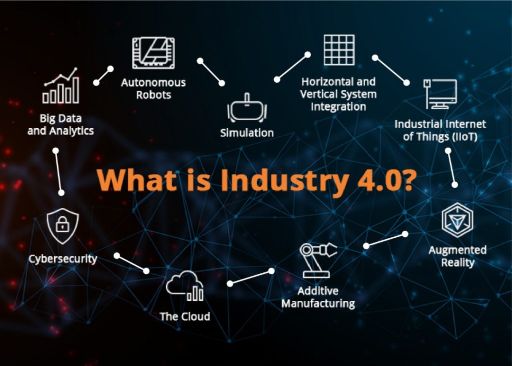
Industry 4.0 Smart Factory refers to the integration of advanced technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, big data analytics, and cloud computing, into the manufacturing ecosystem. This transformation enables autonomous decision-making, real-time data analysis, and seamless communication between machines, systems, and humans.
The Smart Factory concept aims to create a highly flexible, agile, and responsive manufacturing environment that can adapt to changing demands and optimize resource allocation. By connecting various components within the production line, including machines, sensors, and software systems, the Smart Factory enables the seamless exchange of information, enabling faster production cycles, reduced downtime, and improved quality control.
Key Technologies Driving Industry 4.0 Smart Factory
a) Internet of Things (IoT):
The IoT forms the backbone of Industry 4.0, enabling the interconnection and communication between physical devices and systems. By embedding sensors, actuators, and communication modules into machines and equipment, manufacturers can collect real-time data, monitor performance, and enable predictive maintenance.
b) Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML algorithms analyze vast amounts of data collected from IoT devices, enabling intelligent decision-making and automation. From predictive maintenance to quality control and demand forecasting, AI-powered systems optimize production processes, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency.
c) Robotics and Automation:
The integration of robots and automation systems in the Smart Factory enhances production speed, precision, and flexibility. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human operators, performing repetitive tasks, and handling hazardous operations, while autonomous mobile robots streamline material handling and logistics.
d) Big Data Analytics:
By leveraging advanced analytics techniques, manufacturers can extract actionable insights from the vast amount of data generated within the Smart Factory. These insights drive continuous improvement, optimize resource allocation, and enable predictive maintenance.
Benefits of Implementing Industry 4.0 Smart Factory
Implementing an Industry 4.0 Smart Factory offers numerous benefits to manufacturers across various industries. Some of the key advantages include:
a) Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
The Smart Factory leverages automation, real-time data analytics, and intelligent decision-making to optimize production processes. By eliminating manual errors, reducing downtime, and streamlining workflows, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of operational efficiency and productivity.
b) Improved Quality Control:
With advanced sensors and data analytics, the Smart Factory enables real-time monitoring and quality control throughout the production cycle. Manufacturers can detect and rectify defects or anomalies promptly, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
c) Agile and Flexible Manufacturing:
Industry 4.0 technologies enable manufacturers to respond quickly to changing market demands and customize products efficiently. The Smart Factory allows for easy reconfiguration of production lines, rapid prototyping, and just-in-time manufacturing, enabling companies to stay competitive in dynamic market environments.
d) Cost Reduction:
By optimizing resource allocation, minimizing waste, and reducing manual labor requirements, the Smart Factory helps lower production costs. Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of equipment also prevent unexpected breakdowns, reducing costly downtime.
e) Real-time Data-driven Decision-making:
The Smart Factory provides manufacturers with a wealth of real-time data on production, quality, and performance metrics. This data can be analyzed to gain actionable insights and make data-driven decisions, leading to continuous process improvement and strategic planning.
f) Enhanced Workplace Safety:
By automating hazardous or physically demanding tasks, the Smart Factory improves workplace safety and reduces the risk of accidents. Collaborative robots work alongside human operators, minimizing the potential for injuries and creating a safer working environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 and the concept of the smart factory are revolutionizing manufacturing processes. By integrating advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics, companies are able to achieve unprecedented levels of automation, efficiency, and flexibility in their operations. Smart factories enable real-time data analysis, predictive maintenance, and seamless communication across the entire production chain. With these advancements, manufacturers can optimize productivity, reduce costs, and adapt quickly to changing market demands, paving the way for a new era of industrial transformation.

