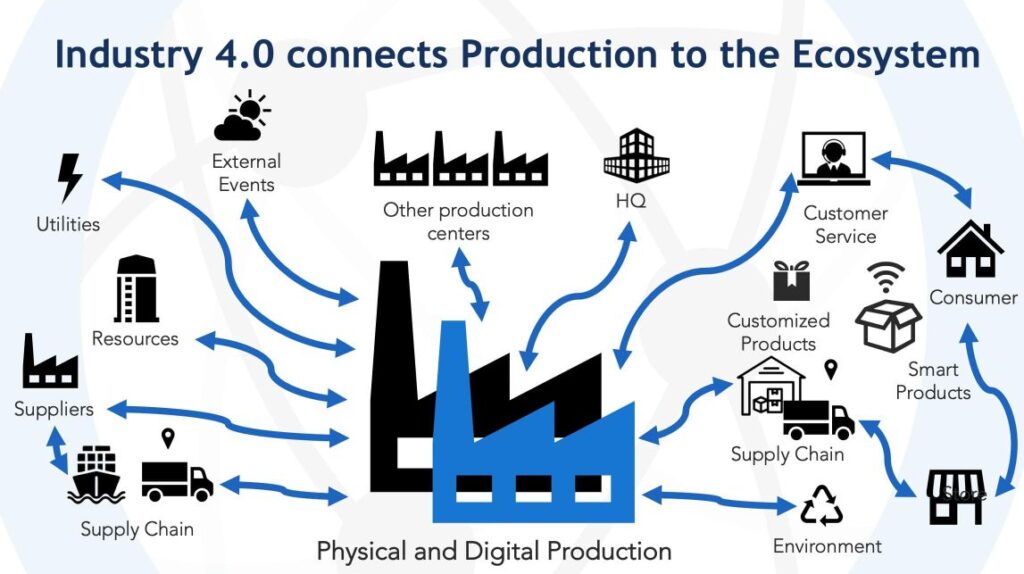
Introduction
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector by integrating digital technologies into traditional industrial processes. The convergence of automation, data exchange, and artificial intelligence has brought forth a new era of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. In this article, we will delve into the impact of Industry 4.0 on manufacturing, exploring the various innovations it has introduced and the challenges it presents to businesses.
Innovations in Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 has ushered in a wave of technological advancements that are transforming the manufacturing landscape. Let’s explore some key innovations:
1. Internet of Things (IoT):
The Internet of Things enables interconnectedness between physical devices and systems, allowing seamless communication and data exchange. IoT devices embedded in manufacturing equipment collect real-time data, providing valuable insights for optimizing processes, predicting maintenance needs, and improving overall efficiency.
2. Big Data and Analytics:
The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices, production processes, and supply chains can be harnessed through big data analytics. Analyzing this data allows manufacturers to gain actionable insights, make data-driven decisions, and uncover patterns for process optimization, predictive maintenance, and quality control.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML technologies enable machines to learn from data, identify patterns, and make autonomous decisions. In manufacturing, AI-powered systems can optimize production schedules, predict equipment failures, and enhance quality control. ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets to improve product design and customer personalization.
4. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized prototyping and production processes. It enables the creation of complex geometries, reduces material waste, and allows for on-demand production. 3D printing accelerates product development cycles and enables customization, making it an invaluable tool in Industry 4.0.
Challenges in Implementing Industry 4.0
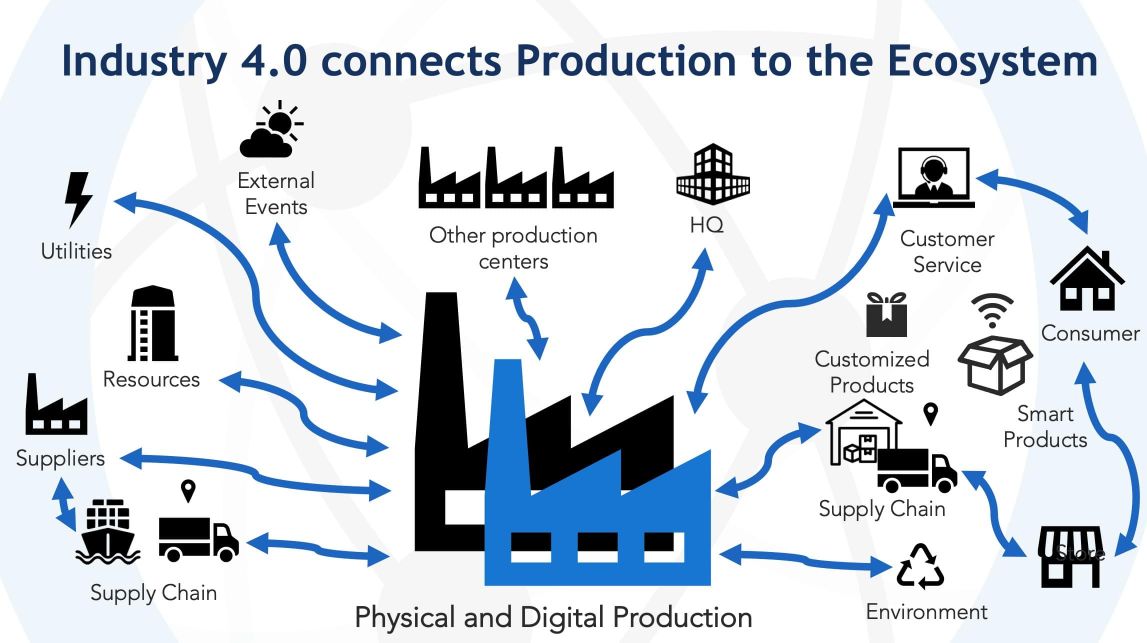
While Industry 4.0 offers numerous benefits, implementing these technologies comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s examine some of the common hurdles:
1. Security Risks:
As manufacturing systems become increasingly interconnected, the risk of cyber threats and data breaches rises. Protecting sensitive data, securing IoT devices, and ensuring network resilience are critical challenges that need to be addressed to safeguard manufacturing operations.
2. Workforce Adaptability:
Transitioning to Industry 4.0 requires upskilling and reskilling the existing workforce to operate and maintain advanced technologies. Companies must invest in training programs to equip employees with the necessary digital skills to thrive in this new era.
3. Cost of Implementation:
Introducing Industry 4.0 technologies can be capital-intensive, requiring significant investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure. Companies must carefully assess the costs and benefits to justify the implementation and ensure a positive return on investment.
4. Data Privacy and Ethics:
With the proliferation of data collection and analysis, ensuring data privacy and ethical use of customer information becomes crucial. Businesses must establish robust data governance policies and comply with relevant regulations to build trust with consumers.
Conclusion
In summary, the impact of Industry 4.0 on manufacturing is profound. The adoption of advanced technologies brings unprecedented opportunities for increased productivity and competitiveness. However, it also poses challenges such as workforce upskilling, cybersecurity risks, and ethical considerations. By understanding and addressing these challenges, manufacturers can harness the full potential of Industry 4.0 while minimizing potential drawbacks.