Introduction
The Future of Manufacturing in the Era of Industry 4.0 holds immense potential for businesses across the globe. This era is marked by the convergence of digital technologies, automation, and data exchange, transforming traditional manufacturing processes into highly efficient and intelligent systems. Industry 4.0 represents a paradigm shift in the manufacturing landscape, offering numerous benefits such as increased productivity, cost savings, and enhanced product quality. In this article, we will explore the key elements of Industry 4.0 and how they are shaping the future of manufacturing.
Smart Factories Foundation of Industry 4.0
Smart factories form the backbone of Industry 4.0. These digitally integrated manufacturing facilities leverage technologies such as IoT, automation, and artificial intelligence to enable seamless communication and collaboration between machines, systems, and humans. Smart factories enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource allocation, leading to optimized production processes and improved overall efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Industrial Automation
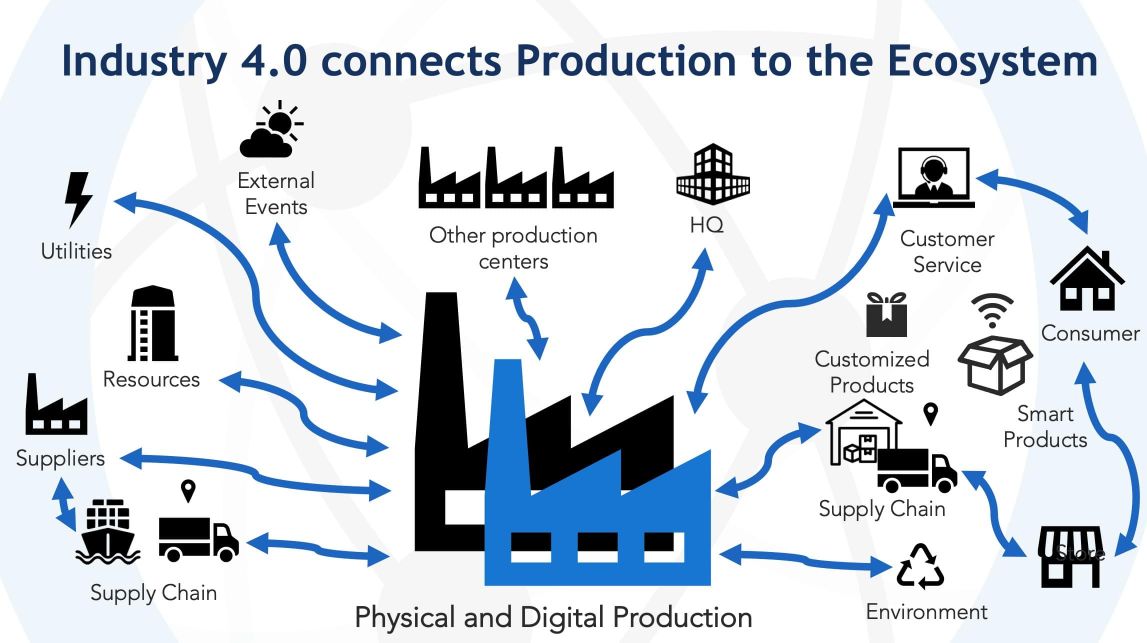
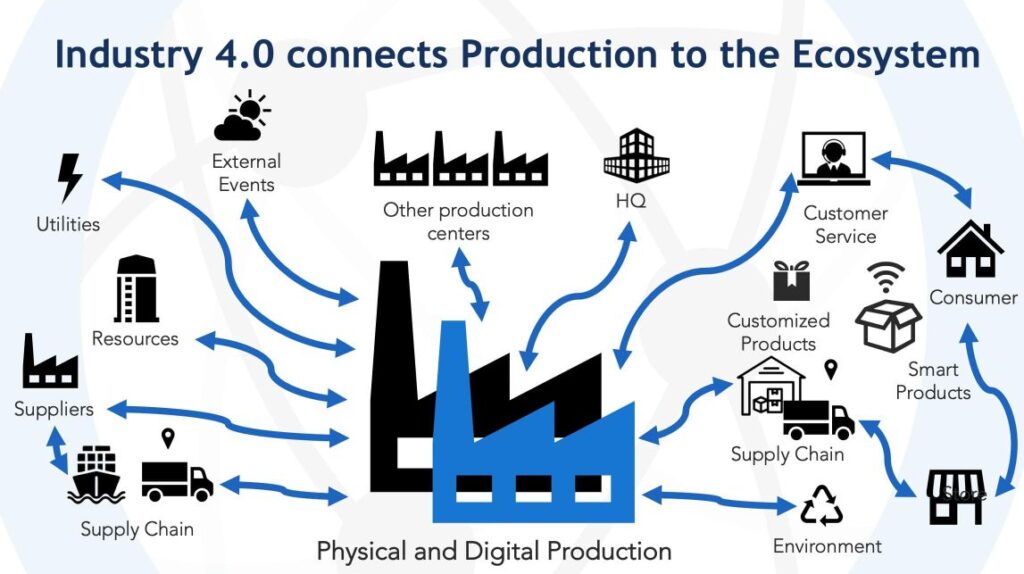
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in Industry 4.0 by connecting various devices and systems within the manufacturing environment. IoT enables the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data, facilitating intelligent decision-making and automation. Industrial automation, driven by IoT, empowers manufacturers to achieve higher levels of productivity, precision, and flexibility. Connected machines and sensors enable remote monitoring and control, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of manufacturing in the era of Industry 4.0 holds tremendous potential for increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation. With advancements such as smart factories, real-time data analytics, and seamless connectivity across the supply chain, manufacturers can expect enhanced agility, customization, and sustainability.