Introduction
Industry 4.0 represents a significant leap forward in the manufacturing sector, revolutionizing the way we produce goods. With advancements in technology, automation, and connectivity, Industry 4.0 is transforming traditional manufacturing processes into intelligent, interconnected systems. This article explores the impact of Industry 4.0 on the manufacturing industry, highlighting the key changes it brings and the opportunities it presents for businesses.
Key Technologies Driving Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is powered by several key technologies that are transforming the manufacturing landscape:
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT connects physical devices and sensors, allowing them to collect and exchange data. In manufacturing, IoT enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make autonomous decisions. In Industry 4.0, AI is used for predictive maintenance, quality control, and intelligent automation.
3. Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics leverages advanced algorithms to extract valuable insights from large datasets. It helps manufacturers optimize processes, detect anomalies, and make data-driven decisions.
4. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources and storage. It enables manufacturers to store and process large volumes of data, collaborate remotely, and scale their operations efficiently.
Benefits and Challenges of Industry 4.0
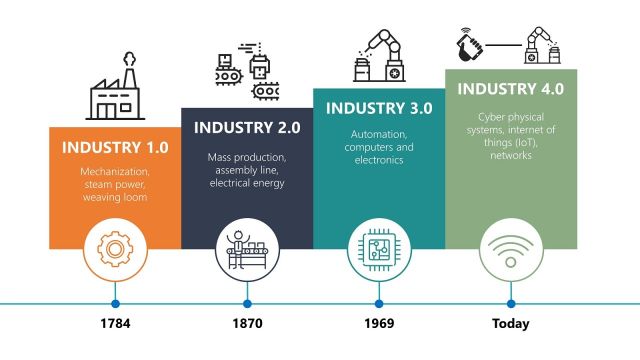
Industry 4.0 brings numerous benefits to the manufacturing industry:
Benefits:
– Increased productivity and efficiency through automation and optimized processes.
– Improved product quality and reduced defects through real-time monitoring and AI-driven quality control.
– Enhanced flexibility and customization by enabling agile manufacturing processes.
– Cost savings through predictive maintenance, inventory optimization, and energy efficiency.
Challenges:
– Integration of legacy systems with new technologies.
– Cybersecurity risks due to increased connectivity.
– Workforce upskilling and adaptation to new roles and responsibilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 is fundamentally transforming the way we make things by introducing intelligent automation, data-driven decision-making, and interconnected systems. This shift towards digitization and connectivity is enhancing manufacturing processes, optimizing resource utilization, and enabling agile responses to market demands.

