Introduction
The fourth industrial revolution, commonly known as Industry 4.0, is reshaping the way industries operate and revolutionizing global manufacturing. This paradigm shift is characterized by the integration of digital technologies and automation into various aspects of industrial processes, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. Industry 4.0 is driven by several key characteristics that define its core principles and objectives.
Connectedness and Interoperability
One of the fundamental characteristics of Industry 4.0 is the extensive connectivity between various components within the industrial ecosystem. Through the Internet of Things (IoT) and other advanced networking technologies, machines, devices, and systems can communicate and share information in real-time. This interconnectedness enables seamless collaboration and coordination across the entire value chain, resulting in improved supply chain management, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes.
Big Data and Analytics
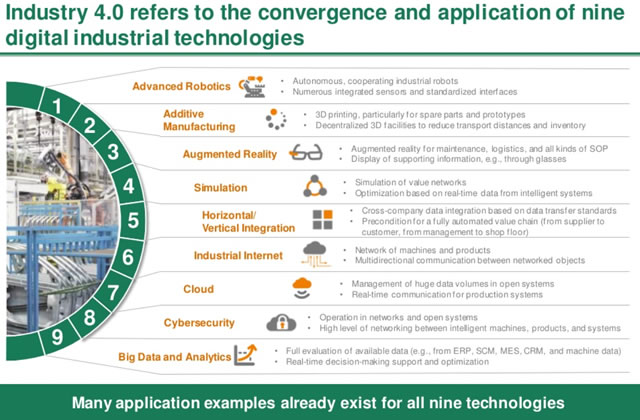
Industry 4.0 generates vast amounts of data from numerous sources, including sensors, machines, and production lines. This data is collected, analyzed, and transformed into actionable insights using advanced analytics techniques. Big data analytics allows manufacturers to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and make data-driven decisions to enhance operational efficiency and quality. The integration of analytics into industrial processes enables predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and optimized resource allocation.
Conclusion
As urbanization accelerates and cities face mounting challenges, Industry 4.0 provides a transformative framework for creating smart cities of the future. By leveraging advanced technologies and digitalization, cities can optimize resource usage, improve services, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents. Embracing the principles of Industry 4.0 and Manufacturing 2.0, we can shape urban environments that are sustainable, resilient, and responsive to the needs of their inhabitants.

