Introduction
The advent of Industry 4.0 has ushered in a new era of manufacturing, revolutionizing traditional factory operations and paving the way for Smart Factories. With the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and robotics, Industry 4.0 Smart Factories are driving unparalleled efficiency, productivity, and flexibility in manufacturing processes.
By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Smart Factories optimize production, enhance quality control, and enable predictive maintenance, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and increased profitability. In this article, we will explore the key components and benefits of Industry 4.0 Smart Factories, as well as address common questions surrounding this transformative concept.
Key Technologies Driving Smart Factories
Industry 4.0 Smart Factories rely on several cutting-edge technologies to transform traditional manufacturing processes:
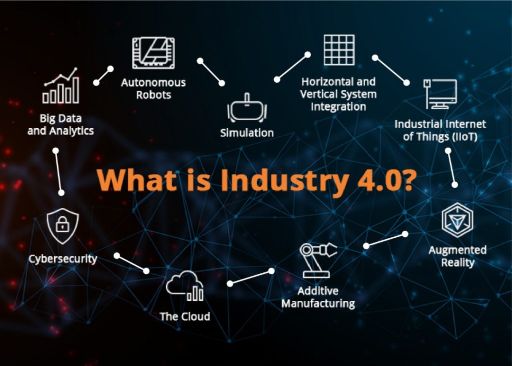
a) Internet of Things (IoT): IoT plays a crucial role in Smart Factories by connecting various devices, machines, and sensors to collect real-time data. This data is then analyzed to optimize production, predict maintenance needs, and enhance overall efficiency.
b) Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms enable Smart Factories to analyze vast amounts of data and make intelligent decisions in real-time. These technologies can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize production processes by autonomously adjusting machine settings.
c) Big Data Analytics: The collection and analysis of big data enable Smart Factories to gain valuable insights into manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and customer behavior. Analyzing this data helps optimize production, improve quality control, and drive innovation.
d) Robotics and Automation: Robots and automated systems play a significant role in Smart Factories. They can handle repetitive tasks, work alongside humans in collaborative environments, and perform complex operations with precision. Robotics and automation enhance productivity
d) Robotics and Automation: Robots and automated systems play a significant role in Smart Factories. They can handle repetitive tasks, work alongside humans in collaborative environments, and perform complex operations with precision. Robotics and automation enhance productivity, reduce errors, and improve worker safety in manufacturing processes.
e) Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms provide the infrastructure to store, process, and analyze the vast amount of data generated in Smart Factories. By leveraging cloud computing, manufacturers can access real-time information from anywhere, enable remote monitoring and control, and facilitate seamless collaboration among teams and stakeholders.
The Future of Smart Factories
The evolution of Industry 4.0 Smart Factories is an ongoing process, with continuous advancements shaping the future of manufacturing:
a) Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML technologies will continue to play a pivotal role in optimizing manufacturing processes. Machine learning algorithms will become more sophisticated, enabling autonomous decision-making and self-optimizing systems.
b) Edge Computing: The implementation of edge computing brings real-time data processing and analysis closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling faster decision-making. Edge computing will enhance the responsiveness and efficiency of Smart Factories by enabling localized data processing and minimizing dependence on cloud infrastructure.
c) Digital Twin Technology: Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets and processes, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize operations. By analyzing data from digital twins, manufacturers can gain valuable insights, improve predictive maintenance, and optimize overall performance.
d) 5G Connectivity: The widespread adoption of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable communication within Smart Factories. With its low latency and high bandwidth capabilities, 5G will support real-time data transfer, facilitate the integration of IoT devices, and enable seamless connectivity among machines, systems, and humans.
e) Sustainability and Green Manufacturing: Smart Factories will increasingly focus on sustainable practices and energy efficiency. The integration of renewable energy sources, smart grids, and energy management systems will help reduce carbon emissions, minimize waste, and contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing ecosystem.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 Smart Factories represent a significant shift in the manufacturing landscape, harnessing advanced technologies to optimize processes, increase productivity, and enhance overall efficiency. By integrating IoT, AI, big data analytics, robotics, and automation, Smart Factories unlock new levels of flexibility, customization, and quality control.
While challenges such as data security, workforce skills, and interoperability need to be addressed, the future of Smart Factories holds immense potential. As technology continues to evolve, Smart Factories will drive innovation, sustainability, and competitiveness in the manufacturing industry, revolutionizing the way products are produced, and improving customer satisfaction.

